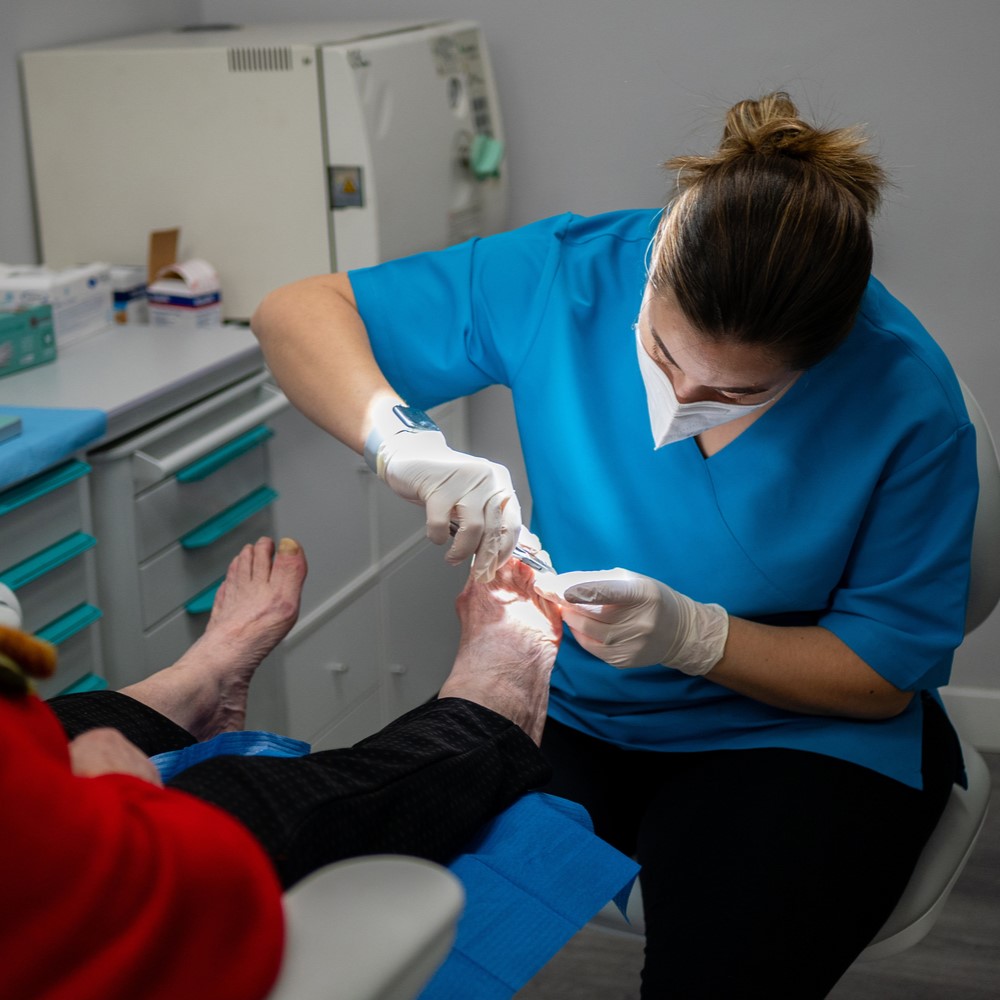
Diabetic foot is a term used to describe a number of foot problems that can occur in people with diabetes. These problems can range from minor skin problems to serious infections and amputations.
How does diabetic foot occur?
Many factors can cause diabetic foot, including:
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves in the feet, leading to a condition called diabetic neuropathy. This can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the feet. It can also make it difficult to feel injuries, such as cuts, blisters, and ulcers.
- Poor blood circulation: High blood sugar levels can also damage the blood vessels in the feet, leading to poor blood circulation. This can make it difficult for the body to heal wounds and fight infections in the feet.
- Foot deformities: High blood sugar levels can also cause changes in the shape of the feet, such as bunions, hammertoes, and flat feet. These deformities can put extra pressure on certain areas of the foot, making them more likely to develop ulcers.
Other risk factors for diabetic foot include:
- Smoking damages the blood vessels and makes it more difficult for wounds to heal. Get medical help to quit smoking.
- Obesity puts extra stress on the feet and makes them more likely to develop ulcers. Tips to lose weight.
- High blood pressure can also damage the blood vessels in the feet. Consult a doctor to help you manage your blood pressure.
- High cholesterol can also damage the blood vessels in the feet. Book an appointment now to keep it under control.
How to prevent diabetic foot
A number of things that people with diabetes can do to prevent diabetic foot, including:
- Control blood sugar levels: Keeping blood sugar levels as close to normal as possible can help to prevent nerve damage and poor blood circulation.
- Inspect the feet daily: People with diabetes should inspect their feet daily for cuts, blisters, and ulcers. If they notice any problems, they should see a doctor right away.
- Wear proper footwear: People with diabetes should avoid wearing high heels or shoes that are too tight or too loose. Find out how to choose the right shoe.
- Practice good foot care: People with diabetes should wash their feet daily in warm water and soap. Diabetic foot care tips.
- See a doctor regularly: People with diabetes should see a doctor for regular foot exams. This will help to identify any problems early on when they are most treatable.
Treatment for diabetic foot
Treatment for diabetic foot will depend on the severity of the problem. For minor problems, such as dry skin or calluses, over-the-counter products may be helpful. For more serious problems, such as ulcers or infections, prescription medications or surgery may be necessary.