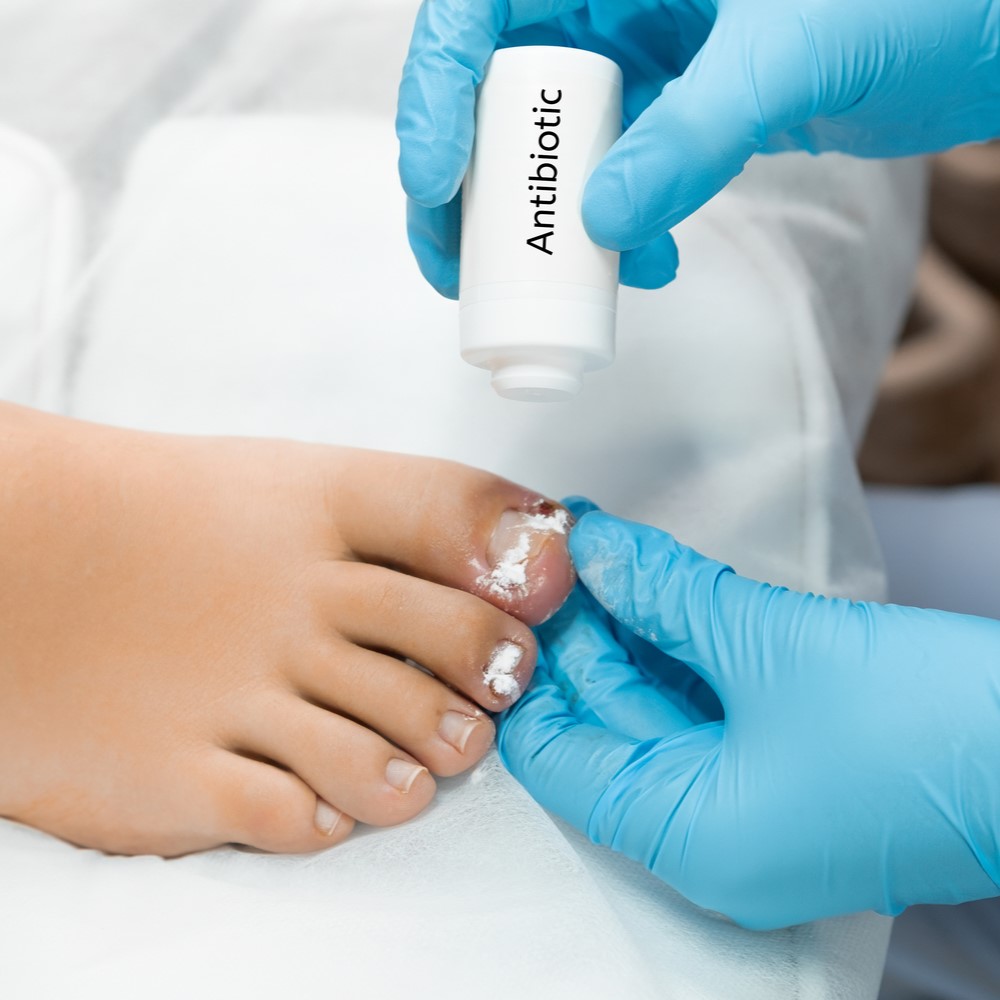
Diabetic foot ulcers are a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to amputation if left untreated. These sores are caused by nerve damage (neuropathy) and inadequate blood supply to the feet. If you have diabetes, it’s crucial to understand the signs of a diabetic foot ulcer and seek prompt medical attention.
Recognizing the Signs
- Painless sores: Diabetic neuropathy can often numb the feet, making it difficult to notice minor cuts or blisters.
- Redness or swelling: These are common signs of infection.
- Drainage: Pus or fluid draining from the sore is a sign of infection.
- Darkened skin: This can indicate tissue death.
Treatment Options
The appropriate treatment for diabetic foot ulcers will depend on the extent of the problem. Common approaches include:
- Offloading: This involves taking pressure off the affected foot to promote healing. It may involve wearing special shoes, braces, or using crutches.
- Wound care: Regular cleaning and dressing of the ulcer are essential to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Debridement: This procedure removes dead or infected tissue from the ulcer.
- Antibiotics, either taken orally or administered intravenously, may be used to treat infections.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged blood vessels or remove infected tissue.
Prevention is Key
Preventing diabetic foot ulcers is crucial. Here are some tips:
- Regular foot exams: Check your feet daily for any signs of injury or infection.
- Practice good foot care by washing your feet daily with warm water and gentle soap. Thoroughly dry them, paying particular attention to the spaces between your toes.
- Diabetic shoes: Wear well-fitting shoes that provide adequate cushioning and support.
- Blood sugar control: Maintaining good blood sugar control is essential for preventing complications like diabetic foot ulcers.
Find out more tips for diabetic foot care.
Additional Tips for Managing Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- See your doctor regularly: If you have diabetes, it’s important to see your doctor for regular check-ups, including foot exams.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can reduce blood flow to your feet and increase your risk of developing diabetic foot ulcers.
- Manage other health conditions: Conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol can also increase your risk of developing diabetic foot ulcers.
- Seek professional help: If you have a diabetic foot ulcer, don’t hesitate to seek help from a podiatrist. Book an appointment now!
If you have diabetes, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. By taking proactive steps to prevent and treat diabetic foot ulcers, you can significantly reduce your risk of complications and improve your overall quality of life.



